
[ad_1]
Amit Binderman discusses changing extracted enamel into osseoinductive bone graft materials
Alveolar bone regeneration is a vital component of dental and maxillofacial surgical procedure, notably for sufferers requiring dental implants or corrective procedures as a consequence of traumatic accidents, periodontal defects, bone loss, or congenital anomalies. Conventional bone grafting strategies have been employed to advertise bone regrowth, however they typically include quite a few limitations — together with irritation on the graft website (international materials response), which hampers therapeutic and impedes regeneration. Many conventional graft supplies don’t resorb, stopping the conversion of the positioning into native bone. Then again, some supplies resorb too quickly, failing to supply enough assist for the longevity of newly fashioned tissue (woven bone). In sure cases, grafting materials is vulnerable to an infection and gentle tissue invagination into the graft itself. Moreover, most supplies don’t combine successfully with surrounding bone or dental implants, making them unpredictable when speedy placement is required. Though these limitations might not be crucial in some instances corresponding to sinus grafting, they considerably have an effect on alveolar bone regeneration procedures, at occasions yielding unpredictable outcomes. Furthermore, these supplies are closely reliant on the general well being situation of the affected person — compromised sufferers like diabetics, people who smoke, and people on treatment don’t reply nicely to many supplies, hindering profitable bone regeneration.
Practitioners who depend on autologous bone, thought-about because the gold commonplace, resort to bone harvesting. Nonetheless, these strategies typically necessitate a secondary harvesting website, leading to potential affected person discomfort, morbidity, and elevated prices. Moreover, harvested bone regularly fails to offer enough quantity for the required process. However, from a organic standpoint, autologous tissue is superior. Autologous tissue possesses osseoinductive and osseoconductive properties, facilitating each bone regeneration and the required scaffold for supporting regenerated bone till it matures into lamellar bone.

A novel method
Prior to now 15 years, a promising idea has been developed by biotechnology firm, KometaBio Inc. (www.kometa bio.com) — the conversion of affected person enamel into autologous dentin grafts. This resolution harnesses the osseoinductive regenerative potential of human enamel. This idea entails changing extracted enamel into osseoinductive bone graft materials, providing a customized and biocompatible choice for alveolar bone regeneration. Given the excessive similarity in composition between enamel and bone, coupled with the attraction of progenitor cells by dentin, grafts derived from enamel exhibit profound bioactivity.
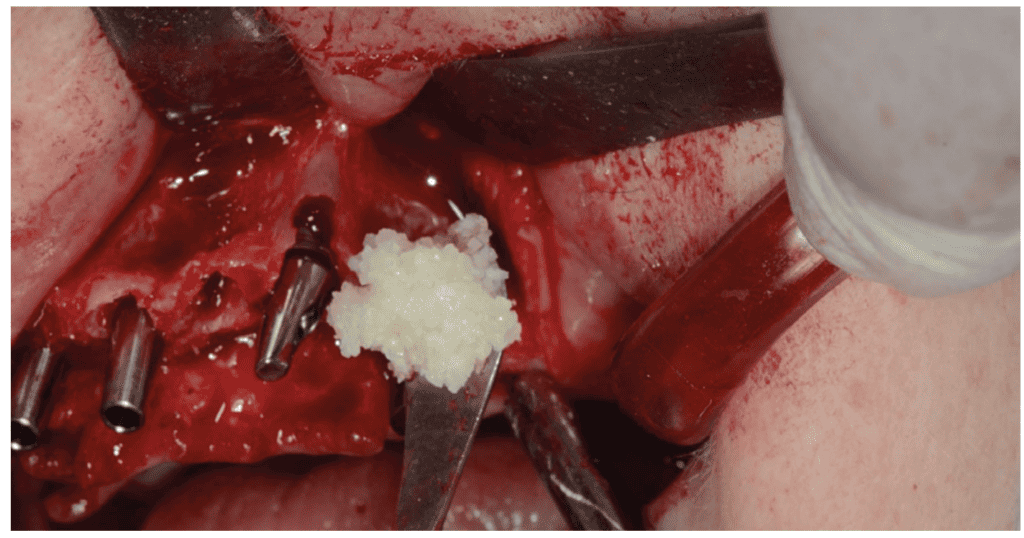
The method begins with the extraction of the affected person’s pure tooth, a routine process carried out by dentists and oral surgeons. The extracted tooth then undergoes mechanical and chemical cleaning to get rid of micro organism, infections, and any restorations corresponding to composites, fillings, or endo supplies (Figures 1A-1B). The tooth is subsequently pulverized into managed particle sizes, presenting a user-friendly putty-like format (Determine 2). The ensuing acellular scaffold retains the architectural and compositional traits of pure bone, making it an excellent substrate for bone regeneration (Determine 3). A tooth, wealthy in HA mineral, collagen fiber sort I, progress elements, and BMPs, presents a wonderful graft materials, additional enhanced by its autologous nature. The HA scaffold steadily resorbs, the collagen contributes to graft osseoinductive properties, and progress elements speed up therapeutic by attracting progenitor cells and signaling M2 macrophages, fostering osteoblastic exercise. A dental assistant or physician can rework any extracted tooth into an autologous dentin graft inside 7-8 minutes chairside, following this protocol.

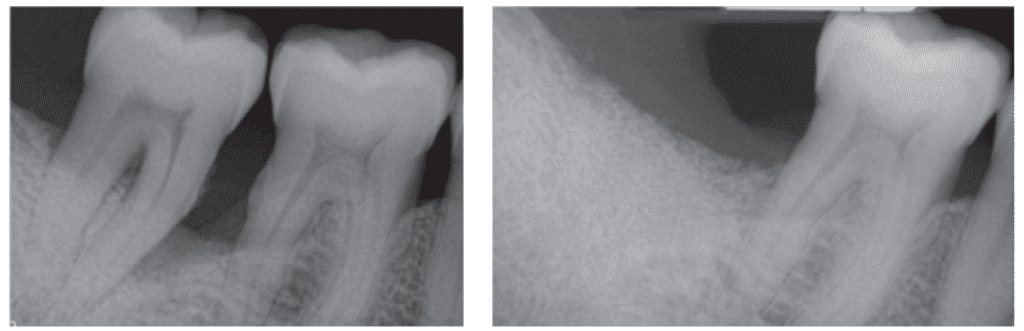
Upon implanting the Dentin Graft, a good microenvironment encourages osteogenic cell migration to the positioning. These cells then differentiate into osteoblasts, the bone-forming cells accountable for synthesizing the bone tissue’s extracellular matrix. This course of mirrors pure bone formation, ensuing within the gradual improvement of purposeful alveolar bone. Over time, the Dentin Graft slowly resorbs, revealing extra collagen and progress elements, finally changing the dentin with native bone after roughly 10-14 months. The newly fashioned bone maintains its dimensional integrity as lamellar bone (Determine 3).
Benefits of Autologous Dentin Graft
The usage of affected person enamel for osseoinductive bone grafting presents a number of notable benefits over conventional grafting strategies:
- Predictability: Essentially the most vital benefit of utilizing an autologous graft, like dentin grafts, is the improved predictability of therapy success. Research point out minimal loss in top and width after grafting with dentin grafts, sustaining horizontal and vertical dimensions near the unique degree.
- Biocompatibility: Because the graft materials originates from the affected person’s physique, the danger of immune rejection and antagonistic reactions is considerably lowered, selling biocompatibility and hastening the pure website therapeutic course of with minimal irritation.
- Lowered morbidity: In contrast to autologous bone, which calls for a secondary surgical website for bone harvesting, teeth-derived grafts negate the necessity for extra invasive procedures, minimizing donor website morbidity and affected person discomfort.
- Enhanced regenerative potential: The inherent osseoinductive properties of teeth-derived grafts facilitate the pure bone formation course of, leading to strong and purposeful bone regeneration.
- Sustainability: Repurposing extracted enamel for bone grafting provides a sustainable method that recycles organic materials that may in any other case be discarded.
- Tender tissue invagination prevention: Autologous dentin grafts exhibit lowered danger of soppy tissue invagination into the graft website, doubtlessly eliminating the necessity for barrier membranes.
- Affected person acceptance: Sufferers, knowledgeable in regards to the autologous use of their very own extracted enamel, typically view grafting procedures extra favorably, rising their willingness to endure the process.
- Price effectivity: Dentin grafts supply an economical graft choice, with a single tooth producing between 1cc – 5cc of grafting materials.
Scientific assist
Over the previous twenty years, greater than 120 research have explored the traits and medical points of dentin grafting. These research have in contrast autologous dentin grafts with typical grafts and examined particular indications. The widespread thread throughout this analysis is the constant achievement of alveolar bone regeneration and upkeep over time by way of dentin grafting.
Conclusion
Bone grafting is more and more prevalent in dentistry, whether or not for extraction socket rehabilitation, alveolar bone reconstruction, or implant success enhancement. The predictability of grafting outcomes performs a pivotal function. Choosing the very best obtainable choices, notably a matrix able to inducing bone formation and performing as a long-term scaffold, is essential. Extracted enamel current an ideal candidate for such a matrix. Whereas enamel have lengthy been used as a substitute graft materials, the advances by KometaBio have streamlined their managed and environment friendly utilization.
[ad_2]