
[ad_1]
Drs. Mathieu Goudal and Cécile Bailly talk about an answer for managing atrophic posterior mandibular areas
To at the present time, the dental implant rehabilitation of atrophic mandibular lateral areas stays a organic, temporal, and monetary problem. Due to CAD/CAM, titanium subperiosteal implants have turn out to be a viable different to standard axial implants and bone regeneration.
Abstract
Subperiosteal implants have a nasty fame attributable to outdated practices. The principle drawbacks — lack of adjustment and biocompatibility — have been corrected utilizing CAD/CAM and titanium. New merchandise have entered the market over the previous few years. The CAD/CAM SUB Implant™ by Panthera Dental, developed in collaboration with Dr. Yvan Poitras, presents an answer in managing atrophic posterior mandibular areas.
Historical past
First described by Dr. Gustav Dahl in 1940, subperiosteal implants allowed for mounted denture rehabilitation for full or posterior edentulism (Class I).1 These implants have been custom-made cobalt-chrome subperiosteal frames with transmucosal abutments to anchor implant-supported dentures. Made-to-measure implants have been created utilizing a direct bone impression after elevating giant, full-thickness flaps. The body was positioned on the residual bone and stabilized utilizing retaining screws, whereas attainable adjustment defects have been corrected by drilling or filling the area with bone substitute.2
Subperiosteal implants had a survival price of fifty% to 60% after 15 years with important complication dangers.3 The shortage of osseointegration and the poor precision of the impression brought on an absence of stability and adaptation of the metallic body and led to an infection, irritation, and bone resorption.4,5 These implants steadily grew to become much less common and have been changed by endosseous implants, which have been extra dependable within the brief and long run.6
Physiopathology of the mandible
Nonetheless, in extreme circumstances of atrophy, denture rehabilitation utilizing axial implants might be very complicated as a result of lack of the alveolar bone. The alveolar bone exists solely for the dental organ, which is the place this bone develops and grows. Tooth, the periodontal ligament, and the alveolar bone are subsequently interdependent.
After edentulism, the labial alveolar bone will steadily lower in top, density, and thickness. The lack of perform of the alveolar bone and the stress it undergoes will trigger resorption that begins within the periosteum, and bone apposition might lower and even stop.7,8 If edentulism isn’t compensated, the alveolar bone will proceed to bear resorption and will even be misplaced utterly. In probably the most critical circumstances of mandibular atrophy, basal bone loss can happen.
Conversely, an alveolar osteolysis attributable to periodontitis results in dental organ loss. Some micro organism concerned in periodontal illness related to unfavorable native and immune components trigger alveolar bone loss that results in edentulism.9 In superior levels, periodontitis may cause full alveolar bone loss, even after edentulism.
This bone loss intensifies with age. The expression of homeogenes and hormones liable for alveolar bone upkeep decreases with age, inflicting decalcification and bone destruction. Denture rehabilitation could also be iatrogenic for the remaining bone, and sporting unstable and poorly tailored detachable dentures might overload the alveolar bone, inflicting resorption as a protection mechanism. A failed implant rehabilitation may improve the lack of residual bone quantity.
Alveolar bone loss follows a predictable sample represented by the Cawood physiopathological classification. This classification permits clinicians to decide on the denture rehabilitation method finest suited to every scenario.10 The edentulous mandible undergoes important resorption and loses 40% to 60% of its top on common. At atrophic levels, the mandibular canal could also be stage with the alveolar ridge, compromising denture rehabilitation.11
Putting axial implants in extreme circumstances of atrophy might require rearranging bone mass by guided bone regeneration, distraction osteogenesis, or crestal reconstruction by bone grafting.12-14 With these implant surgical procedures in atrophic areas, there are dangers of hemorrhage and lesions to neighboring anatomical and nervous constructions.
The outcomes of mandibular bone quantity reconstruction are pretty unpredictable, because the spongy bone is dense and the cortical bone is thick, thereby lowering blood circulate and regenerative potential. It’s a lengthy, costly approach that requires two surgical procedures with important therapeutic durations: one for crestal reconstruction and one other for implant placement. Success relies upon closely on the surgeon’s expertise with the process.
For the rehabilitation of atrophic posterior mandibular areas, subperiosteal implants are an alternate value exploring. Putting this implant is technically easier for the surgeon and might be achieved in a single process with a shorter therapeutic interval.
Anatomy evaluate and surgical method
The mandible is characterised by the presence of the mandibular canal containing the inferior alveolar nerve, together with venous, arteries, and lymphatic vessels. This canal enters the mandible at its ramus by the mandibular foramen, runs by the physique of the mandible, and exits by the psychological foramen. The inferior alveolar nerve is the motor for the anterior stomach of the digastric and the mylohyoid muscular tissues. It additionally provides sensation for mandibular enamel, the decrease lip, and the chin. The pathway of the mandibular canal is variable and should bear preoperative examination by analyzing a CBCT.
The lateral facet of the posterior area of the mandible presents the exterior indirect ridge and is the insertion for the cutaneous muscular tissues of the cheek. Its medial facet is linked to the ground of the mouth fashioned by the mylohyoid and geniohyoid muscular tissues, in addition to the tongue. It presents the inner indirect ridge, the insertion level for the superior pharyngeal constrictor, the pterygomandibular ligament, and the mylohyoid muscle in continuity with the periosteum.
This space is adjoining to the submandibular and sublingual areas, that are wealthy in neurovascular constructions.
The submandibular area is characterised by the presence of the submandibular salivary gland, the hypoglossal nerve (XII, motor nerve of the tongue), the lingual nerve, the facial and lingual artery, and the facial and superior thyroid veins. The sublingual area, situated between the ground of the mouth and the mylohyoid muscle, incorporates the sublingual salivary gland, the deep-lingual vein, the hypoglossal nerve (style and tongue sensation, visceral motor of the salivary glands), and the submandibular duct15 (Determine 1).

Surgical procedure within the posterior area of the mandible is delicate as a result of proximity of the sublingual and submandibular areas and the presence of the inferior alveolar nerve. Two full-thickness flaps are mirrored to entry the underlying bone. The crestal incision must separate the residual keratinized gingiva in two equal vestibular and lingual parts. Posteriorly, the releasing incision have to be made towards the anterior border of the mandibular ramus to keep away from reducing the lingual nerve. Anteriorly, the vestibular incision should go across the psychological foramen to protect the inferior alveolar nerve and prolong towards the symphysis for laxity with no releasing incision.
Throughout implant surgical procedure on the posterior area of the mandible, two important priorities have to be taken under consideration when elevating flaps: pushing again the sublingual area wealthy in neurovascular constructions and avoiding injury to the mylohyoid muscle, which might result in communication between the oral cavity and the submandibular area. This might result in a hemorrhage obstructing the higher aerodigestive tract.16 Putting axial implants is restricted within the atrophic posterior mandibular area as a result of proximity of the inferior alveolar nerve within the physique of the mandible and the chance of nerve damage it may trigger.
The Panthera SUB subperiosteal implant, proven under, is a viable therapy choice on this scenario. It’s achieved in a single surgical procedure: the proximity of the inferior alveolar nerve to the alveolar crest and the low bone quantity accessible usually are not a contraindication.
Traits and design of the SUB implant
The Panthera SUB implant is produced by Panthera Dental (Québec) and was developed by Dr. Yvan Poitras (Québec).
Knowledge assortment is just like that carried out when planning axial implants:
- a CBCT
- a recording of the dental and mucosal surfaces
- a mock-up
The standard and precision of the CBCT are vital and the primary components figuring out how precisely the subperiosteal implant adapts to the bone floor. It’s subsequently essential to optimize the dental X-ray tools settings to acquire high-resolution photographs with sufficient distinction to visualise the bones in different constructions. Furthermore, a large discipline permitting for a single go of the molar zone to be implanted, the ipsilateral ramus posteriorly, and the symphyseal area as much as the contralateral canine is a minimal requirement. Stitching (overlapping a number of “narrow-field” photographs) is strongly discouraged, given the dangers of distortion. Lastly, the information have to be exported to the common DICOM format.
A traditional bodily impression that’s later scanned by a laboratory scanner or a local digital picture utilizing an intraoral digicam permits for preliminary dental and mucosal surfaces to be recorded. The file have to be exported to STL or PLY format.
A bodily or digital mock-up should match up with the dental and mucosal surfaces. The surgeon and technician use the protocol with which they’re most acquainted (totally digital workflow, twin scan with radiopaque markers, and many others.).
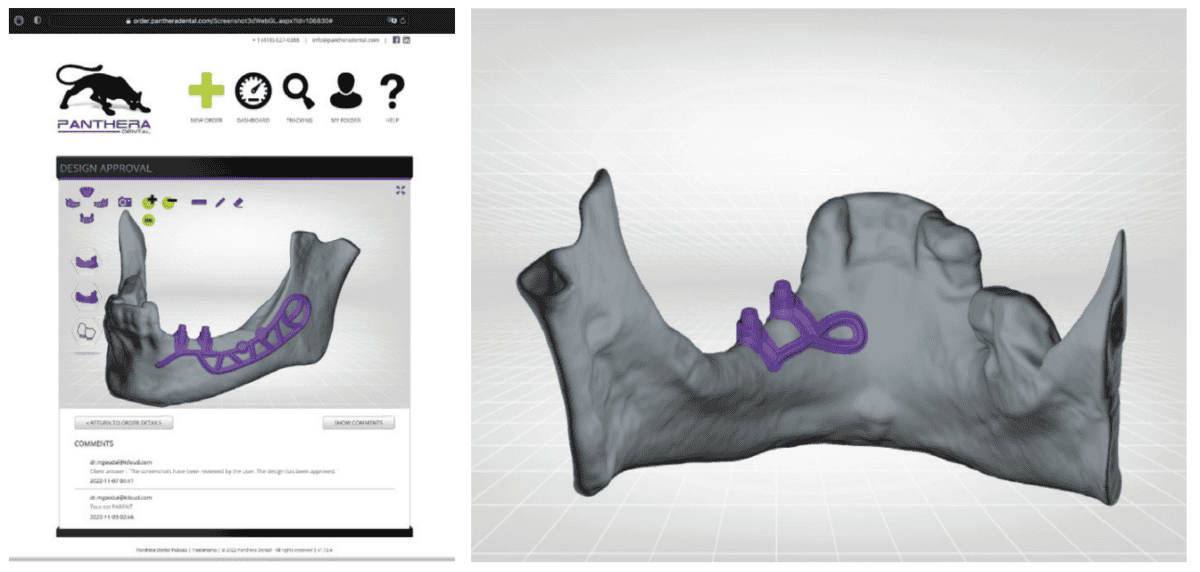
This information is recorded on the Panthera order platform. Utilizing a easy step-by-step course of, the clinician can point out the variety of enamel to get replaced, the specified place of the prosthetic platforms, and many others. As soon as the order has been positioned and the information despatched, the dashboard can be utilized to trace the progress of the work:
- affirmation of knowledge receipt
- affirmation of knowledge high quality
- fusion of three-data layers
- implant design proposal
- validation by the surgeon
- implant manufacturing
- implant delivery
Panthera designers use proprietary software program to carry out a exact fusion of the three information sorts. The design is produced in-house in line with the surgeon’s order and in accordance with the mock-up, all whereas following the identical blueprint: Within the vestibular area, the skeleton extends anteriorly by an arm going across the emergence of the inferior alveolar nerve, posteriorly by a loop as much as the outer floor of the mandibular ramus. Within the lingual area, the body stops distally in vertical alignment with probably the most distal prosthetic platform and apically over the mylohyoid ridge. Nonetheless, a loop extends the implant to the symphyseal area of the mandibular. Lastly, the exterior indirect ridge, which is extremely corticalized, is the anchoring location for osteosynthesis screws (Figures 2A and 2B).
After validation by the surgeon, five-axis CNC milling machines with a precision of 5 µm (far superior to the acquisition of the CT scan) produce subperiosteal implants in disks manufactured from Ti6Al4V ELI (Grade 23), a titanium-aluminum-vanadium alloy that’s purer than the usual Ti6Al4V alloy. After machining, the floor involved with the bone and the periosteum is sanded.
The mixture of the next three traits obtain higher outcomes for subperiosteal implants in comparison with conventional methods:
- biocompatible materials
- exact adjustment (CT scan, CAD/CAM, machining)
- tough floor
Medical case and planning
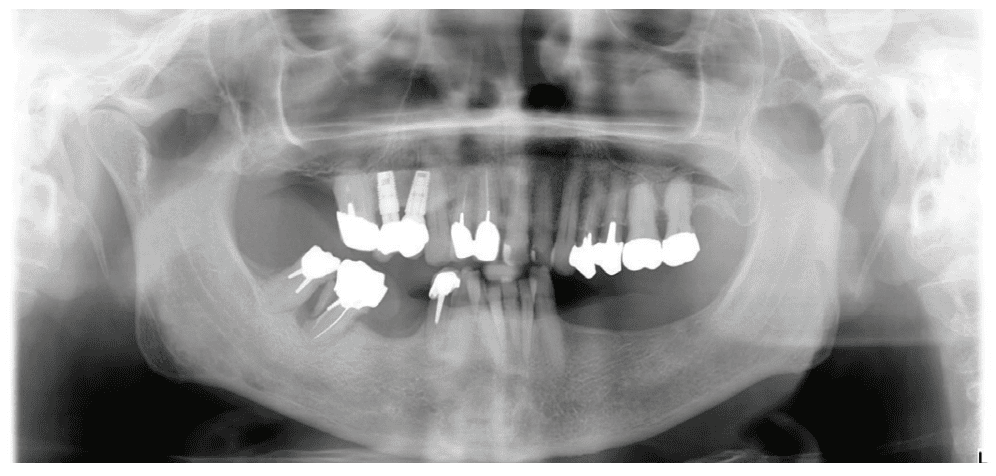
Our affected person is consulting for ache in the proper mandibular molar area and issue chewing (Determine 3).
Her historical past is kind of widespread: discomfort, adopted by a failure to put on the detachable denture with a metallic framework, and at last neglecting take care of household causes. At age 77, she is completely wholesome sufficient for oral surgical procedure. Nonetheless, she would favor to not bear lengthy and complicated implant therapy. Her request is before everything practical. Esthetics and value are secondary issues. We subsequently provide the next therapy plan: hold the malpositioned anterior mandibular enamel with solely gentle gingivitis, rehabilitate the left posterior mandibular area with a subperiosteal implant, extract molars 47 and 48, and reassess the most effective implant resolution for this area after therapeutic.
Given the preliminary anatomical scenario (robust resorption, important cellular tender tissue, blockage by the tongue, V-shaped mandible), a traditional impression with a CIT and a bodily mock-up with radiopaque markers are most popular.
Knowledge is exported to the Panthera platform, and we obtain a design proposal inside a couple of days. The visualization instruments permit us to scroll freely within the three-dimensional reconstruction space. Every aspect (implant, mock-up, bone) might be seen individually, hidden, made opaque or clear (Figures 2A, 2B, 4A, 4B, and 4C). The proposal is validated by the surgeon for the implant to be produced and shipped.

As soon as it’s obtained, the implant is cleaned, decontaminated, and sterilized on the dental workplace.
Surgical process
The process begins with native anesthesia at a number of factors, vestibular and lingual, from the symphyseal area to the ascending ramus. Nonetheless, an infiltration within the lingula of the mandible isn’t obligatory. The incision is carried out utilizing the approach described above (Figures 5A and 5B).
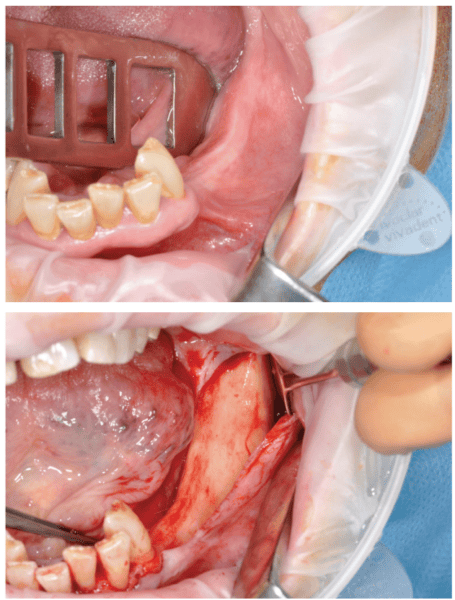
It’s crucial to fastidiously replicate a full-thickness flap following the periosteum. After reflection, an atraumatic periosteal enlargement utilizing a tender brush (Determine 6) will permit for the flaps to be repositioned with out rigidity over the implant and bony surfaces on the finish of the process.

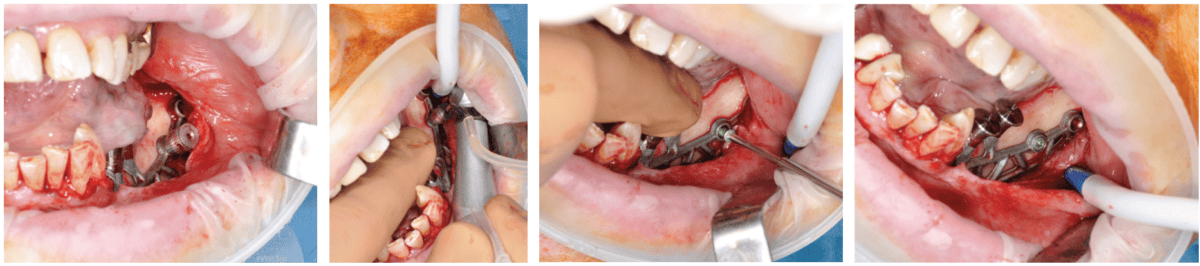
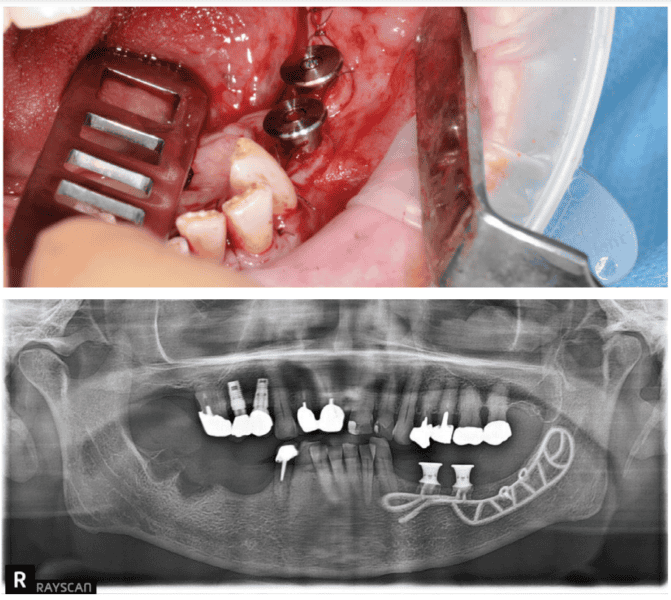
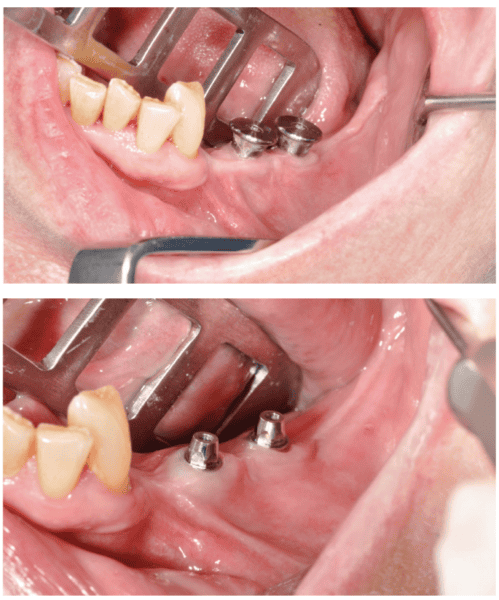
After the tender tissue is ready, the bony floor is fastidiously cleaned. For straightforward insertion, the therapeutic abutments are left in place, and the implant is held firmly with hemostatic forceps (Determine 7). The implant is inserted through distal translation within the path of the angle of the mandible, then a mesio-anterior rotation. The surgeon should management the dearth of mobility and the variation of the implant to the bony floor in any respect factors (Figures 8A, 8B, 8C, and 8D).


To make sure the implant is steady in the course of the osseointegration interval, an osteosynthesis screw is positioned within the ready area (Figures 9A, 9B, 9C, and 9D).
The flaps are fastidiously repositioned and sutured with out rigidity with Halsted and over-and-over sutures (Figures 10A and 10B).
Therapeutic and osseointegration
Osseointegration takes 4 months to finish and happens by two mechanisms:
- First by direct contact of the bone with the tough titanium end of the internal floor of the implant
- Subsequent by progressive bone apposition on the equally tough outer floor. The truth is, the passive repositioning of the flap on the finish of the process creates an area between the periosteum (internal floor of the flap) and the implant positioned over the bone the place the blood clot might be trapped (Determine 11).17-19

The affected person returns 4 months later for a scientific follow-up (Figures 12A and 12B) and X-rays (Determine 13).

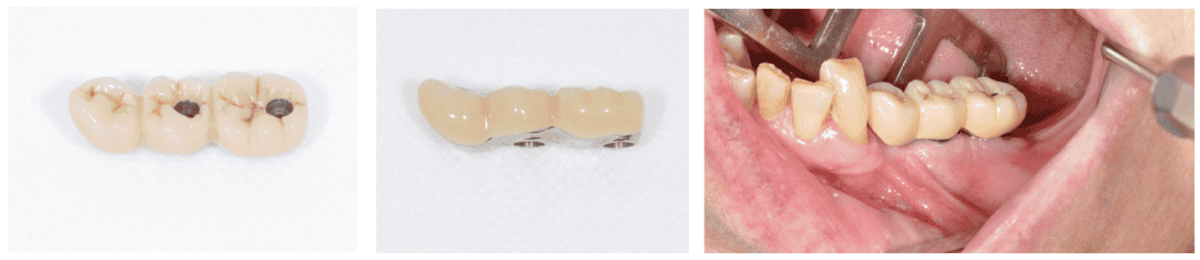
The everlasting dentures are then positioned over a titanium body processed by Panthera Dental and stratified in composite on the denture laboratory (Figures 14A-14C).
Literature evaluate and success price
We’re on the stage the place we will see if the survival charges of subperiosteal implants have improved in comparison with extra widespread methods corresponding to mandibular grafts for implant rehabilitation of atrophic posterior mandibular areas. The systematic literature evaluate under compares the scientific outcomes of those two methods and justifies using CAD/CAM subperiosteal implants.
Supplies and technique
The literature evaluate was carried out utilizing the PRISMA protocol standards. Searches occurred in March 2021 utilizing the PubMed, DOSS, Embase, and Cochrane databases, and it was break up into two elements:
- A search targeted on mandibular subperiosteal implants utilizing the next key phrases: “subperiosteal implant” and (“CAD/CAM” or “3D printing” or “direct metallaser sintering” or “additive manufacture”) and “dental implantation, subperiosteal” [MeSH Terms] and “computer-aided design” [MeSH Terms].
- A search targeted on inlay bone grafts utilizing the next key phrases: “mandible” and “vertical ridge augmentation” and “sandwich osteotomy” OR “inlay bone graft” or “interpositional bone graft” and “alveolar ridge augmentation” [MeSH Terms] AND “mandible” and “alveolar bone atrophy” [MeSH Terms] and “bone grafting” [MeSH Terms] OR “mandibular osteotomy” [MeSH Terms].
Outcomes
These searches discovered 30 articles assembly the choice standards for this literature evaluate: 5 on subperiosteal implants20–24 and 25 on inlay grafts.25–49 By analyzing the outcomes, we will measure the implant survival price (variety of sufferers who didn’t lose any implants/whole variety of sufferers). Among the many 86 sufferers who participated in research on subperiosteal implants, three misplaced an implant attributable to recurring infections. The implant survival price between 8 months to three years is 96.5%. For inlay grafts, implant survival is dependent upon the success of the graft. Among the many 345 sufferers who participated in research, 28 grafts failed, and subsequently no implants may very well be positioned. Two research didn’t specify the variety of sufferers, however quite the variety of implants when calculating the survival price. The variety of sufferers subsequently decreases from 345 to 250. Amongst these sufferers, 19 misplaced a number of implants, for an implant survival price of 92.5% between 8 months and 5 years.
Dialogue
Analyzing these articles exhibits promising survival charges for the rehabilitation of atrophic posterior mandibular areas utilizing subperiosteal implants. These articles are few, and their stage of proof is low. Most are scientific case reviews with few sufferers (lower than 100) with short-term follow-ups. Lengthy-term scientific research with a excessive stage of proof are required to reaffirm the true success of subperiosteal implants in a scientific setting.
Various parts have been unable to be assessed on this evaluate, together with the implant success price, which is a greater predictor of the long-term effectivity of implant-supported rehabilitation. Nonetheless, the few prosthetic and biologic issues reported within the examine appear to point excessive success charges for subperiosteal implants. In comparison with inlay graft methods, these implants have the benefit of requiring a single surgical procedure with a brief therapeutic interval and few postoperative and prosthetic issues, making them a dependable and promising different.
Conclusion
Due to CAD/CAM, Panthera SUB subperiosteal implants clear up most points encountered (lack of adjustment, two procedures, and many others.) with their conventional counterparts. Furthermore, utilizing biocompatible titanium as a substitute of cobalt-chrome permits for a real osseointegration of the implant. Lastly, the literature tends to indicate good outcomes with this system in treating posterior mandibular edentulation.
[ad_2]